Golfer’s Elbow

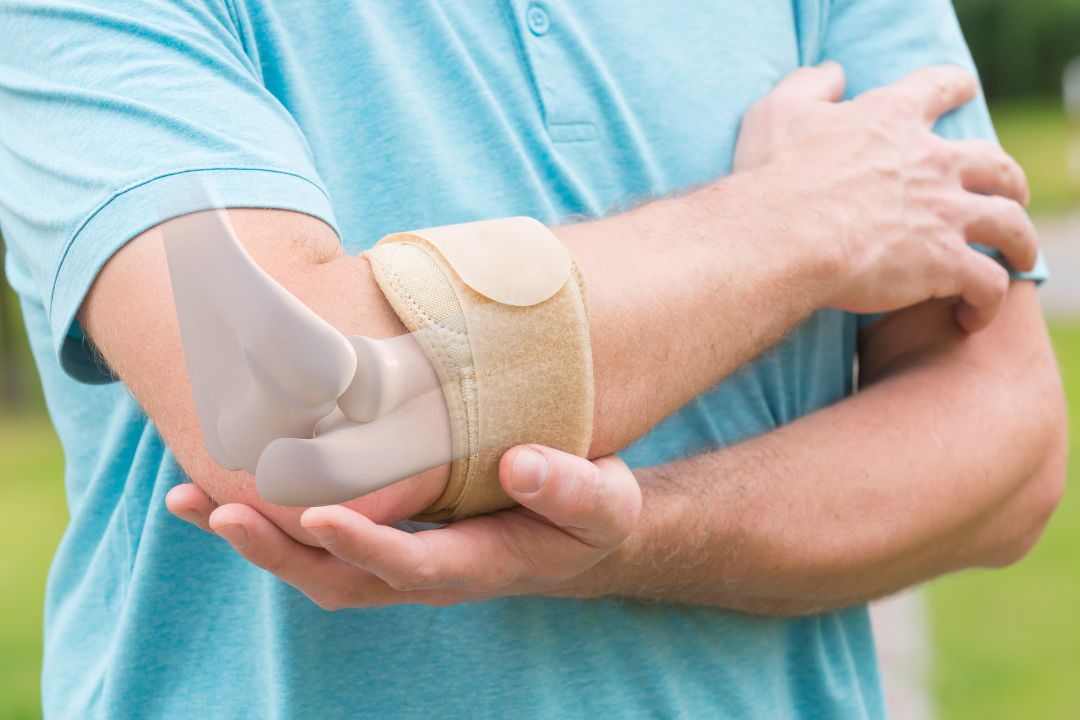
What is Golfer’s Elbow
Golfer’s Elbow is medically known as medial epicondylitis. This common overuse injury affects the tendons on the inner side of the elbow and can impact individuals beyond the realm of golf, reaching those engaged in various activities involving repetitive gripping, wrist flexion, and forearm rotation.
Causes of Golfer's Elbow
Golfer’s Elbow develops when tendons attaching to the inner elbow’s bony bump undergo overuse and damage. Key causes include:
- Repetitive Stress : Activities like golf, racquet sports, weightlifting, or tool usage, involve repetitive wrist and forearm motions.
- Poor Technique : Incorrect equipment or techniques in sports or daily tasks can stress tendons.
- Muscle Imbalances : Weakness or imbalances in the forearm and upper arm muscles increase susceptibility.
- Aging : Tendons become less flexible and more prone to damage with age.
Symptoms of Golfer's Elbow
Symptoms can vary in severity and include:
Pain on the Inner Elbow
Tenderness near the medial epicondyle.
Weakened Grip Strength
Noticeable decrease in grip strength.
Stiffness
Difficulty flexing and extending the affected arm fully.
Numbness and Tingling
Sensations radiating down the forearm.
Diagnosis
Seek a medical evaluation if Golfer’s Elbow is suspected. An orthopedic specialist can diagnose through a physical examination and, if necessary, imaging tests like X-rays or an MRI to rule out other potential causes.
Treatment Options
Treatment focuses on relieving the pain, promoting healing, and preventing further injury. Options include:
- Rest : Avoid activities aggravating the condition to allow tendons to heal.
- Ice and Compression : Reduce swelling and alleviate pain.
- Anti-Inflammatory Medications : Over-the-counter NSAIDs for pain relief.
- Physical Therapy : Customized exercise programs to improve strength, flexibility, and biomechanics.
- Bracing : Supportive braces or splints to reduce strain on tendons.
- Steroid Injections : Injections, to reduce inflammation and pain, are used sparingly due to potential side effects.
- Platelet-Rich Plasma (PRP) Therapy : Injecting a concentrated solution of the patient's platelets to promote healing.
- Shockwave Therapy : Using sound waves to stimulate healing in chronic cases.
- Surgery : Considered when conservative treatments fail, involving the removal of damaged tissue or reattaching tendons.
Preventing Golfer's Elbow
Prevention is the key for individuals at risk. Please consider the following to prevent Golfer’s Elbow:
- Proper Technique : Ensure correct form and techniques.
- Warm-up and Stretching : Adequate warm-up and stretching exercises before arm and wrist-intensive activities.
- Strengthening Exercises : Strengthen forearm and upper arm muscles to reduce the risk.
- Equipment Check : Use well-suited, properly maintained equipment.
Conclusion
Golfer’s Elbow affects people from various backgrounds, but understanding its intricacies, symptoms, and treatments is crucial for effective management. If Golfer’s Elbow is suspected or there is persistent elbow pain, seek prompt medical attention for an accurate diagnosis and appropriate care. With the right treatment and preventive measures, most individuals can make a full recovery from Golfer’s Elbow and resume their favorite activities pain-free.